Purging gas lines is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient gas distribution systems. It involves removing air, moisture, and contaminants through open-end, closed-end, or vacuum purging techniques. This process requires safety precautions, including PPE, ventilation, and following manufacturer guidelines. By utilizing a purging machine, flow meter, and pressure gauge, gas lines are isolated, pressurized or vacuumed, and monitored until readings meet specified limits. Successful purging prevents airlocks, protects equipment, enhances safety, improves system efficiency, and reduces maintenance costs.
Purging Gas Lines: An Essential Maintenance Procedure for Safe and Efficient Gas Distribution
Ensuring the safe and efficient operation of gas distribution systems is paramount. One crucial maintenance procedure that plays a pivotal role in achieving this is gas line purging. Purging involves removing air pockets, water vapor, and contaminants from gas lines, preparing them for hydrostatic testing, and preventing corrosion.
Importance of Purging Gas Lines
Gas line purging is an indispensable procedure that serves multiple critical purposes. Air pockets can form when gas lines are installed or repaired, creating blockages that disrupt gas flow and potentially leading to dangerous equipment malfunctions. Water vapor, if present in the gas line, can condense and freeze, causing further flow obstructions and even damage to sensitive equipment. Additionally, contaminants such as dust, debris, or welding residue can accumulate within gas lines, interfering with the proper flow of gas and reducing system efficiency.
Purging Methods and Equipment
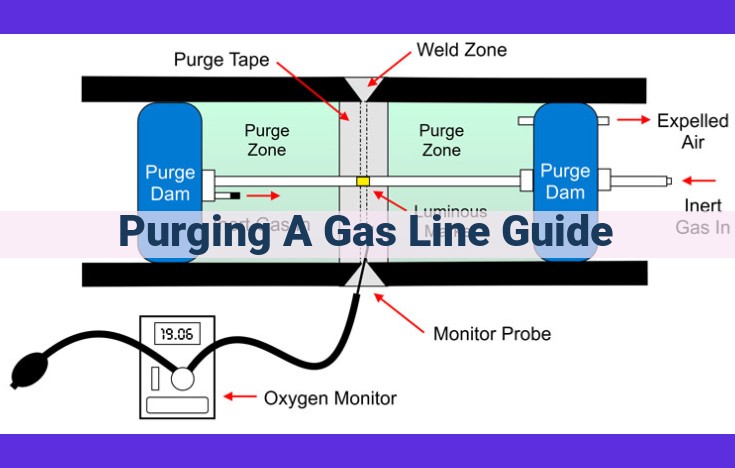
Various methods exist for purging gas lines, each tailored to specific circumstances. Open-end purging involves allowing gas to flow through the line with one end open, while closed-end purging seals both ends and pressurizes the line with an inert gas. Vacuum purging uses a vacuum pump to evacuate air and contaminants from the line. Inert gases like nitrogen or helium are commonly used for purging, as they are non-flammable and do not react with the gas being transported.
The equipment required for gas line purging typically includes a purging machine, flow meter, pressure gauge, and other accessories. The purging machine generates the flow or vacuum necessary for the purging process. The flow meter measures the rate of gas flow, while the pressure gauge monitors the pressure within the line.
Safety Precautions for Gas Line Purging
Purging gas lines involves working with flammable gases, so safety is of utmost importance. Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety glasses, and respirators should be worn at all times. Adequate ventilation is crucial to prevent the accumulation of gas fumes in the work area. Additionally, manufacturers’ guidelines and industry best practices for gas line purging must be strictly adhered to.
Completion Criteria for Gas Line Purging
The success of gas line purging is verified by monitoring specific parameters. The flow meter should indicate a stable and consistent flow rate, while the pressure gauge should show the desired pressure within the line. These readings must meet predefined limits established by industry standards or manufacturer specifications.
Benefits of Purging Gas Lines
Thoroughly purging gas lines offers numerous benefits that enhance system performance and safety. By removing air pockets and ensuring proper gas flow, purging prevents equipment damage and extends its lifespan. It also eliminates the risk of airlocks, ensuring a continuous and uninterrupted supply of gas. Furthermore, purging protects pipelines from corrosion by removing moisture and contaminants that could potentially lead to deterioration. Regular gas line purging is a cost-effective way to minimize maintenance requirements and improve system efficiency, reducing downtime and maximizing productivity.
Reasons for Purging Gas Lines
- Removal of air pockets, water vapor, and contaminants.
- Preparation for hydrostatic testing and corrosion prevention.
Reasons for Purging Gas Lines: Ensuring Safe and Efficient Operation
Purging gas lines is a crucial procedure that ensures the safe and efficient operation of gas distribution systems. It involves removing air pockets, water vapor, and contaminants that can accumulate in the lines over time, compromising the integrity and performance of the system.
Removal of Air Pockets
Air pockets in gas lines can create blockages that restrict gas flow and interfere with the proper operation of equipment connected to the system. Purging expels these air pockets, ensuring a continuous and uninterrupted flow of gas throughout the distribution network.
Eliminating Water Vapor and Contaminants
Water vapor can condense in gas lines, leading to corrosion and rust, affecting the structural integrity of the pipes and potentially causing leaks. Similarly, contaminants such as dirt, dust, and debris can clog filters and valves, disrupting gas flow and reducing system efficiency. Purging helps remove these impurities, minimizing their negative impact on the system.
Preparation for Hydrostatic Testing and Corrosion Prevention
Purging is also an essential step in preparing gas lines for hydrostatic testing, a procedure that tests the integrity of the pipes by pressurizing them with water. Removing air and contaminants before hydrostatic testing prevents false readings and ensures accurate assessment of the line’s condition. Additionally, purging helps remove moisture from the lines, reducing the risk of corrosion and extending the lifespan of the system.
Purging Gas Lines: Essential Methods for Safety and Efficiency
In the realm of gas distribution, maintaining the integrity and efficiency of gas lines is paramount. Proper purging procedures play a vital role in ensuring the safe and reliable operation of these systems. Several methods exist to effectively purge gas lines, each tailored to specific situations and requirements.
Open-End Purging: A Straightforward Approach
Open-end purging involves allowing a continuous flow of gas through the line to displace any trapped air or contaminants. As the gas flows, it exits through an open downstream end, sweeping away impurities and leaving behind pure gas. This method is particularly useful for purging relatively short lines.
Closed-End Purging: Trapping Impurities
Closed-end purging involves pressurizing the line with an inert gas such as nitrogen. The sealed downstream end traps any lingering air or contaminants, which are then removed using a vacuum pump. This method is suitable for purging longer lines or those containing sensitive equipment, as it minimizes the escape of gas into the atmosphere.
Vacuum Purging: Removing Impurities Thoroughly
Vacuum purging, as its name suggests, employs a vacuum pump to create a negative pressure within the line. This draws out air and contaminants, leaving a vacuum that is then backfilled with the desired gas. Vacuum purging is highly effective in removing stubborn impurities and is often used prior to hydrostatic testing or when the line contains critical components.
Inert Gases and Vacuum Pumps: Essential Tools
Inert gases such as nitrogen play a key role in purging gas lines. Their non-reactive nature ensures they do not react with gas or line materials, making them safe and suitable for use in enclosed spaces. Vacuum pumps, on the other hand, generate the necessary suction to remove air and contaminants, ensuring thorough purging.
Safety Precautions for Gas Line Purging: A Crucial Guide for Your Protection
Purging gas lines is a critical maintenance procedure that ensures the safe and efficient operation of gas distribution systems. However, it also involves potential hazards, making safety a top priority. Here are crucial precautions you must take during gas line purging:
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Always wear appropriate PPE when handling gas lines. This includes:
- Hard hat: Protects your head from falling objects.
- Eye protection: Shields your eyes from chemicals and debris.
- Gloves: Prevents contact with hazardous materials.
- Respiratory protection: Protects your lungs from toxic fumes.
Ventilation
Proper ventilation is essential to prevent the buildup of hazardous gases. Ensure:
- Adequate airflow throughout the work area.
- Use fans or open doors and windows to create ventilation.
- Never smoke or use open flames near gas lines.
Manufacturer’s Guidelines
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the specific purging equipment and gas line system. These guidelines provide essential safety measures, such as:
- Proper equipment handling procedures.
- Safe pressure limits for the gas line.
- Specific purging techniques for the system.
Other Important Precautions
- Inspect the gas line thoroughly before purging to identify any potential leaks or damage.
- Inform others in the area that gas line purging is taking place.
- Use only trained and qualified personnel to handle gas line purging.
- Monitor the purging process closely and be prepared to respond to any emergencies.
By adhering to these safety precautions, you can ensure a safe and successful gas line purging operation. Remember, safety is paramount when working with hazardous materials like natural gas, and it should never be compromised.
Tools and Equipment for Efficient Gas Line Purging
Gas line purging is a critical maintenance procedure that ensures the safe and efficient operation of gas distribution systems. To perform this task effectively, it’s essential to have the right tools and equipment.
Purging Machine
The purging machine is the central component of the gas line purging process. It generates the necessary vacuum or pressure to remove contaminants from the line. Purging machines come in different sizes and capacities, so it’s important to select the appropriate one based on the size and condition of the gas line.
Flow Meter
The flow meter measures the rate of flow of gas through the line. This information helps ensure that the purging process is progressing as expected. The flow meter can also be used to detect any leaks or restrictions in the gas line.
Pressure Gauge
The pressure gauge monitors the pressure within the gas line. The readings from the pressure gauge help determine the completion of the purging process and ensure the system is operating within safe parameters.
Other Necessary Equipment
In addition to the purging machine, flow meter, and pressure gauge, other equipment may be necessary, such as:
- Rubber hoses for connecting the purging machine to the gas line
- Fittings to adapt the hoses to the purging machine and gas line
- Safety glasses and gloves for personal protection
- Instruction manual for the purging machine to ensure proper operation and safety precautions
Line Isolation and Equipment Connection: A Crucial Step in Purging Gas Lines
Purging gas lines is a crucial maintenance procedure for ensuring their safe and efficient operation. A critical step in this process involves isolating the line and connecting the necessary equipment. Isolation prevents gas flow from entering or exiting the line during purging. The equipment includes purging machines, flow meters, pressure gauges, and safety devices to monitor and control the process.
Pressurization and Vacuum Creation: Removing Impurities and Creating a Controlled Environment
Once the line is isolated, pressurization or vacuum creation begins. Pressurization involves introducing an inert gas or air into the line to displace any remaining contaminants. Vacuum purging involves creating a vacuum within the line to draw out impurities. Both methods effectively remove air pockets, water vapor, and other contaminants that can impair gas flow.
Monitoring and Gas/Air Release: Ensuring Safety and Efficiency
During pressurization or vacuum creation, monitoring is essential to ensure that the purging process is proceeding as planned. Flow meters and pressure gauges provide real-time data on the gas flow rate and pressure. By monitoring these parameters, technicians can identify any deviations or potential issues. Gas and air are released at specific points along the line to facilitate the removal of contaminants. This step involves careful monitoring and controlled release to maintain a safe and efficient purging process.
Purging Gas Lines: A Vital Maintenance Procedure
In the intricate web of gas distribution systems, purging gas lines is a crucial maintenance procedure that ensures the safe, efficient, and reliable operation of these systems. It is a meticulous process that involves the removal of air pockets, water vapor, and various contaminants from gas pipelines.
Reasons for Purging Gas Lines
The primary reasons for purging gas lines are threefold:
- Ensuring proper gas flow: Air pockets can disrupt gas flow, leading to operational inefficiencies and potential safety hazards. Purging removes these pockets, allowing gas to flow smoothly and consistently.
- Preparation for hydrostatic testing: Hydrostatic testing involves pressurizing gas pipelines with water to identify leaks or weak points. Purging removes air and moisture from the lines, creating a more accurate testing environment.
- Corrosion prevention: Moisture and certain contaminants can cause corrosion in gas pipelines, leading to leaks and premature failure. Purging eliminates these corrosive elements, extending the lifespan of the lines and ensuring optimal performance.
Methods of Purging Gas Lines
There are three main methods for purging gas lines:
- Open-end purging: Gas is introduced into one end of the line while the other end is open, allowing contaminants to escape.
- Closed-end purging: Gas is introduced and pressurized in the line with both ends closed, forcing contaminants out through release valves.
- Vacuum purging: A vacuum is created in the line to draw out contaminants before introducing gas.
Safety Precautions for Gas Line Purging
Purging gas lines involves working with flammable gases, so safety precautions are paramount:
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) including gloves, eye protection, and respiratory protection.
- Ensure proper ventilation to prevent gas accumulation.
- Follow manufacturer’s guidelines and industry best practices.
Tools and Equipment
Essential tools and equipment for gas line purging include:
- Purging machine
- Flow meter
- Pressure gauge
- Vacuum pump (for vacuum purging)
- Inert gases (nitrogen or carbon dioxide)
Steps Involved in Gas Line Purging
The steps involved in purging gas lines are:
- Line isolation: Isolate the section of the line to be purged.
- Equipment connection: Connect the purging machine and other equipment to the line.
- Pressurization/vacuum creation: Introduce inert gas or create a vacuum to purge the line.
- Monitoring: Monitor flow meter and pressure gauge readings to ensure the process is progressing as expected.
- Gas/air release: Vent any remaining gas or air from the line through release valves.
Completion Criteria for Gas Line Purging
The purging process is considered complete when:
- The flow meter readings indicate a stable gas flow rate.
- The pressure gauge readings are within the specified range.
Benefits of Purging Gas Lines
Purging gas lines offers numerous benefits:
- Prevents airlocks and ensures proper gas flow.
- Protects equipment from damage and extends lifespan.
- Enhances safety by eliminating potential hazards.
- Improves system efficiency and reduces maintenance costs.
By adhering to proper purging procedures, gas distribution companies can ensure the reliable and safe operation of their systems, delivering gas to consumers without interruption.
Benefits of Purging Gas Lines
Gas line purging is an essential maintenance procedure that brings a multitude of advantages to gas distribution systems. By removing air pockets, water vapor, and contaminants, purging ensures the safe and efficient operation of these systems. The benefits of purging gas lines extend to protecting equipment, enhancing safety, and optimizing system performance.
Prevention of Airlocks and Proper Gas Flow
Air pockets, known as airlocks, can obstruct the flow of gas, leading to operational inefficiencies. Purging eliminates these airlocks, allowing for unrestricted gas movement throughout the system. This not only improves gas delivery but also prevents pressure fluctuations and potential system failures.
Protection of Equipment and Extended Lifespan
Gas lines are susceptible to corrosion and damage from moisture and contaminants. Purging removes these harmful elements, protecting equipment from premature deterioration. By extending the lifespan of gas lines and associated components, purging reduces the need for costly repairs and replacements.
Enhanced Safety and Hazard Elimination
The accumulation of air and contaminants can create potential safety hazards in gas distribution systems. Purging eliminates these hazards by removing any combustible or explosive materials. This proactive maintenance measure reduces the risk of accidents and ensures a safer operating environment for personnel and the surrounding community.
Improved System Efficiency and Reduced Maintenance Costs
A well-purged gas line operates more efficiently, reducing energy consumption and minimizing maintenance requirements. By preventing airlocks and protecting equipment, purging optimizes system performance and reduces the need for costly repairs. This translates into lower operating costs and a more reliable gas distribution system.