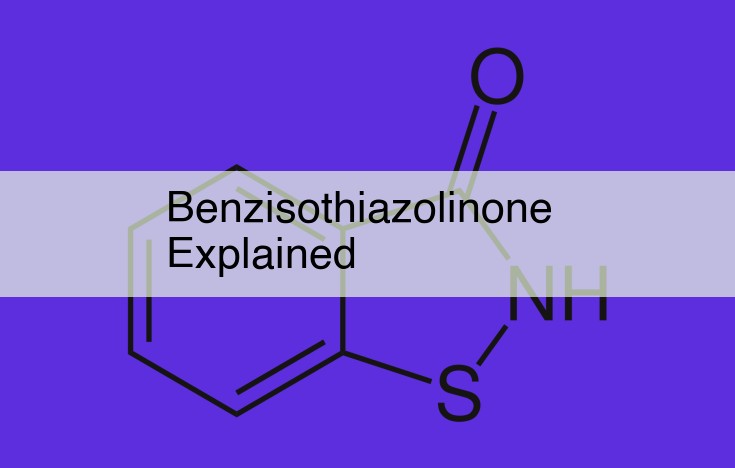
Benzisothiazolinone (BIT), a broad-spectrum preservative, is a heterocyclic organic compound used in personal care products, industrial fluids, paints, and more. Its antimicrobial activity stems from its ability to disrupt cell metabolism. Despite its widespread use, BIT raises safety concerns due to its potential for skin irritation and allergic reactions, leading to regulations limiting its usage. Alternative preservatives, such as phenoxyethanol, offer comparable antimicrobial properties with reduced health risks. However, BIT’s effectiveness, ease of use, and cost-efficiency continue to make it a common choice in various industries.
Benzisothiazolinone (BIT): A Double-Edged Sword in the World of Preservation
In the realm of protecting our beloved products from the onslaught of microbial invaders, Benzisothiazolinone (BIT) has emerged as a formidable warrior. This chemical sentinel stands guard in a wide array of products, from shampoos and conditioners to paints and industrial fluids, keeping harmful bacteria and fungi at bay.
Definition and Structure: The Essence of BIT
Benzisothiazolinone is an organic compound with a distinctive chemical structure. Its molecular backbone features a six-membered ring adorned with a sulfur atom and a nitrogen atom, creating a unique fingerprint that distinguishes it from other preservatives. This structural complexity endows BIT with remarkable stability and antimicrobial prowess.
Applications in Diverse Industries: A Versatile Protector
BIT’s versatility extends far beyond its humble origins as a mere preservative. It finds widespread use in a myriad of industries, including:
- Personal care products: BIT safeguards shampoos, conditioners, and cosmetics against bacterial and fungal contamination, ensuring their safety and efficacy.
- Industrial products: In paints, detergents, and adhesives, BIT combats the growth of microorganisms that could otherwise compromise product quality and longevity.
Safety Concerns: A Delicate Balance
While BIT has proven to be an effective preservative, it does not come without potential drawbacks. Exposure to BIT can trigger adverse reactions in sensitive individuals, ranging from eye irritation and skin allergies to respiratory problems. To mitigate these risks, stringent regulations govern BIT’s use, ensuring that it is employed responsibly and within safe limits.
Alternative Preservatives: Seeking Greener Options
In recent years, concerns have emerged regarding the environmental impact of BIT. Its poor biodegradability and toxicity to aquatic organisms have prompted scientists to explore alternative preservatives with a gentler footprint on the planet. These alternatives, such as benzoic acid and sorbic acid, offer similar antimicrobial protection without the associated environmental concerns.
Benzisothiazolinone (BIT) remains a widely used preservative, offering effective protection against microbial contamination in a diverse range of products. However, its potential health and environmental concerns necessitate careful consideration and the exploration of more sustainable alternatives. By striking a balance between preservation and safety, we can harness the benefits of BIT while mitigating its potential drawbacks, ensuring the well-being of both humans and the planet.
Chemical Properties and Mechanism of Action of Benzisothiazolinone (BIT)
Unveiling the Stealthy Preservative
Benzisothiazolinone, or BIT, is a ubiquitous preservative found in a myriad of everyday products. Its presence ensures the longevity of our shampoo, paints, and household cleaners, but how does this chemical guardian work its magic?
Chemical Unraveling
BIT is a heterocyclic compound with a distinctive structure: a benzene ring fused with a thiazoline ring. This unique architecture grants it water solubility and a pungent odor, characteristics that facilitate its application in various water-based products.
Disrupting Cell Life
The antimicrobial power of BIT lies in its ability to disrupt cell metabolism. Upon contact with microorganisms, it penetrates their cell membranes and seeks out vital targets within. BIT inhibits essential enzymes responsible for cellular respiration, effectively cutting off the energy supply of the invading organisms.
Selective Warfare
BIT exhibits selective toxicity, primarily targeting bacteria and fungi while leaving human cells relatively unharmed. This property makes it a valuable ally in the preservation of products without posing significant health risks to consumers.
Environmental Concerns
While effective in its role, BIT’s poor biodegradability raises environmental concerns. Its persistence in the environment can potentially impact aquatic ecosystems, particularly organisms at the base of the food chain. Responsible use and proper disposal are crucial to minimize its impact on our planet.
Benzisothiazolinone (BIT): A Versatile Preservative in Diverse Industries
In the realm of preservation, benzisothiazolinone (BIT) stands as a robust guardian against microbial threats. This broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent finds its way into a mesmerizing array of products, safeguarding them from degradation and ensuring their safety and efficacy.
Aromatic Delights: Preserving Personal Care Products
From fragrant shampoos to soothing body lotions, BIT plays a vital role in preserving the pristine nature of personal care products. Its ability to combat a wide range of bacteria and fungi ensures that these daily essentials remain fresh and free from harmful microbes.
Industrial Might: Protecting Industrial Products
In the industrial realm, BIT’s prowess extends to protecting paints, coatings, and adhesives. Its exceptional resistance to harsh conditions makes it an indispensable ally in safeguarding these products from deterioration. By inhibiting microbial growth, BIT prevents the formation of unwanted odors and ensures the integrity of these vital materials.
A Hygienic Haven: Maintaining Household Products
The cleanliness of our homes hinges on the efficacy of household products. BIT steps up to the challenge, guarding cleaning solutions, laundry detergents, and disinfectants from microbial contamination. Its broad-spectrum activity ensures that these essential products effectively eliminate germs, leaving homes sparkling and sanitary.
Safety Concerns and Regulations
Potential Health Risks:
- BIT can cause eye irritation, especially in sensitive individuals.
- It may trigger allergic reactions in some people, ranging from mild skin rashes to severe respiratory issues.
Regulations and Restrictions:
- European Union (EU): BIT is regulated under the European Cosmetics Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009. It is allowed for use in cosmetic products at a maximum concentration of 0.1% (as BIT or its sodium salt).
- United States (US): The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has classified BIT as a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) substance for use in food and beverages at a maximum concentration of 0.05%.
- Canada: Health Canada allows the use of BIT as a preservative in personal care products, cosmetics, and certain food applications. However, it is not permitted in over-the-counter (OTC) drug products.
It’s important to note that these regulations and concentrations are subject to change based on ongoing research and risk assessments. Consumers are advised to read product labels carefully and follow usage guidelines to minimize potential exposure risks.
Alternative Preservatives: Safer Choices for You and the Environment
When it comes to preserving products, benzisothiazolinone (BIT) has been a widely used preservative. However, concerns about its potential health risks and environmental impact have led to increased demand for safer alternatives.
One popular option is sodium benzoate, a salt of benzoic acid. It is effective against bacteria and fungi but is less irritating to the skin than BIT. Potassium sorbate is another natural preservative derived from sorbic acid. It is particularly suitable for acidic products like food and beverages.
For products prone to mold and yeast growth, propionic acid is a valuable choice. It is often used in bakery products and dairy items. Calcium propionate is a related compound with similar antimicrobial properties.
Ethylhexylglycerin is a versatile preservative with both antimicrobial and antifungal activity. It is commonly used in personal care products, especially those intended for sensitive skin. Phenoxyethanol is another synthetic preservative that is effective against a wide range of microorganisms. It is often paired with other preservatives to enhance efficacy.
Each alternative preservative has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, sodium benzoate can alter the taste of certain foods, while propionic acid may have an unpleasant odor. By carefully researching and selecting the appropriate preservative, manufacturers can ensure product safety and shelf life without compromising consumer health or the environment.
The Environmental Impact of Benzisothiazolinone (BIT)
Benzisothiazolinone (BIT), a widely used preservative, has raised environmental concerns due to its potential harm to aquatic organisms and its poor biodegradability.
Toxicity to Aquatic Life
BIT’s toxicity to aquatic organisms has been a source of concern. Studies have shown that it can be lethal to fish, crustaceans, and algae even at low concentrations. The mechanism of toxicity is not fully understood, but it’s believed that BIT interferes with cell metabolism by inhibiting enzymes and blocking energy production.
Poor Biodegradability
Another environmental concern is BIT’s poor biodegradability. It breaks down slowly in the environment, which means it can persist for a long time. This persistence can lead to bioaccumulation, where BIT accumulates in the tissues of organisms and can have harmful effects over time.
Environmental Impact
The poor biodegradability and toxicity of BIT can have a negative impact on aquatic ecosystems. It can reduce biodiversity by killing or weakening aquatic organisms. Additionally, it can disrupt the food chain and affect the overall balance of the ecosystem.
The environmental impact of benzisothiazolinone is a growing concern. Its toxicity to aquatic organisms and poor biodegradability highlight the need for more sustainable alternatives. As we continue to use BIT in various products, it’s crucial to take steps to mitigate its environmental impact and protect our valuable aquatic ecosystems.