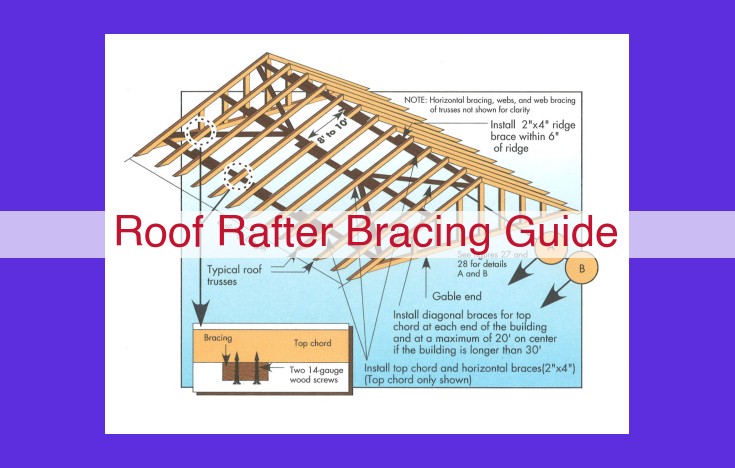
This comprehensive guide on roof rafter bracing provides detailed information on various bracing mechanisms, including rafter braces, tie rods, and cross braces. It explores different rafter support systems, such as collar beams, ridge boards, valley rafters, and hip rafters. Specialized rafters, like jack rafters and common rafters, are also discussed. Additionally, the guide covers roof framing components like gable ends and framing squares, as well as roof covering materials such as roof sheathing, underlayment, and roofing.
- Highlight the critical role of roof rafter bracing in ensuring structural integrity.
- Overview of the different types of roof rafter bracing techniques.
Your roof is a crucial part of your home, providing shelter and protection from the elements. But what many homeowners don’t realize is that the integrity of your roof relies heavily on the strength of its rafters. These beams form the framework of your roof, and without proper bracing, they can become unstable and compromise the safety of your home. That’s where roof rafter bracing comes in.
Roof rafter bracing techniques are essential for ensuring the structural integrity of your roof. They prevent rafters from spreading apart, twisting, or collapsing, which can lead to damage or even collapse of your roof. There are various types of roof rafter bracing techniques available, each with its own advantages and applications.
Types of Roof Rafter Bracing Techniques
Rafter Braces
Rafter braces are horizontal or diagonal beams that connect rafters to prevent lateral movement. They act like struts, providing additional support and keeping rafters from buckling or sagging.
Tie Rods
Tie rods are tension members that connect rafters across the width of the roof. They prevent rafters from spreading apart, especially under weight loads such as snow or wind.
Cross Braces
Cross braces are diagonal beams that connect rafters at their midpoints. They provide additional lateral stability and prevent rafters from twisting or rotating.
In addition to these basic bracing techniques, there are also specialized rafter support systems and components that contribute to the overall stability of your roof. These include:
- Collar beams: Horizontal beams that connect rafters at their top ends, providing support and distributing weight.
- Ridge boards: Beams that connect rafters at the peak of the roof, providing structural support and stability.
- Valley rafters: Beams that support roof surfaces at intersections, preventing them from sagging.
- Hip rafters: Beams that form the hip of the roof, providing support and connecting rafters at angles.
By understanding the different types of roof rafter bracing techniques and their importance, you can ensure that your roof remains strong, secure, and able to withstand the challenges of the elements for years to come.
Rafter Bracing Mechanisms: The Unsung Heroes of Your Roof’s Structural Integrity
Ensuring the longevity and stability of your roof goes beyond the visible elements like shingles and flashing. Behind the scenes, a network of essential components works harmoniously to withstand external forces and maintain the structural integrity of your home. Among these unsung heroes are rafter bracing mechanisms, the backbone of your roof’s ability to resist lateral forces.
Rafter Braces: The Strength Behind the Scenes
Rafter braces are the primary actors in the world of rafter support. These diagonal or horizontal members, installed perpendicular to your rafters, provide crucial lateral support, preventing rafters from buckling or swaying under external pressures. Their role is akin to the supportive arms of a trusted confidant, ensuring that your rafters can carry their load without compromising the roof’s overall stability.
Tie Rods: Keeping Rafters in Their Place
Tie rods are essentially metal tension members that extend across the span of your roof, connecting opposite rafters. Their primary purpose is to prevent rafters from spreading apart under the weight of the roof covering and any accumulated snow or debris. Imagine them as the invisible force that pulls rafters together, ensuring they work as a cohesive unit.
Cross Braces: Enhancing Lateral Stability
When additional lateral stability is required, cross braces step into the picture. These diagonal members are installed between rafters to form an X-shaped pattern, providing extra resistance to lateral forces. Their strategic placement creates a rigid framework, allowing your roof to withstand wind loads and other lateral pressures with ease.
By implementing these rafter bracing mechanisms, you’re essentially creating a strong and resilient roof structure that can withstand the test of time and external forces. So, while you may not see them from the ground, rest assured that these hidden heroes are diligently working to keep your roof safe and sound.
Rafter Support Systems: The Pillars of Roof Stability
In the realm of roof construction, rafters stand tall, the skeletal framework upon which the weight of the roof rests. But what provides these rafters with the unwavering strength to withstand nature’s relentless forces? The answer lies in a carefully devised system of supports, each element playing a pivotal role in maintaining the roof’s structural integrity.
Collar Beams: The Unseen Guardian
Beneath the roof’s exterior, concealed like a hidden treasure, lie collar beams, the unsung heroes of rafter support. These horizontal beams connect opposite rafters at their midpoint, forming an inverted “V” shape. Their presence creates a truss-like structure, transferring the load from the rafters to the supporting walls, ensuring that the roof remains firmly in place.
Ridge Boards: The Spinal Column of the Roof
As the apex of the roof, the ridge board serves as its spinal column, connecting rafters at their highest point. Like a master conductor, it directs the flow of forces, preventing rafters from sagging under the weight of the roof covering. This crucial component also provides a solid base for the installation of roofing materials, creating a watertight seal.
Valley Rafters: Guardians of the Intersections
Where roof planes meet, creating valleys, valley rafters take center stage. These diagonal beams provide crucial support at these vulnerable points, ensuring that the roof can withstand the downward force of snow and water accumulation. Their intricate connections with the ridge board and other rafters form a network of strength, safeguarding against potential failures.
Hip Rafters: The Cornerstones of Hip Roofs
In hip roofs, where the roof slopes meet at a hip, hip rafters emerge as the cornerstone elements. These diagonal rafters extend from the ridge to the corners of the roof, connecting to the valley rafters and jack rafters. Their presence ensures that the roof maintains its shape and integrity, even under extreme weather conditions.
By understanding the intricate interplay of these rafter support systems, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable engineering behind every stable roof. These carefully designed components work in harmony, providing the necessary strength and support to withstand the test of time and the elements, ensuring the safety and comfort of those sheltered beneath.
Specialized Rafters:
- Jack Rafters:
- Explain their significance in hip roof framing and their connection with hip rafters.
- Discuss related concepts like common rafters.
- Common Rafters:
- Describe their function in supporting roof surfaces and their installation.
- Discuss their connection with jack rafters.
Specialized Rafters: The Hidden Players in Roof Framing
In the intricate world of roof framing, there are unsung heroes known as specialized rafters. They play a vital role in shaping and supporting your roof, particularly in hip roofs where the roof slopes up to form a hip.
Jack Rafters: The Pillars of Hip Roofs
Jack rafters are like the reliable comrades of hip rafters. They form the shorter sides of the triangular roof surfaces, supporting the hip rafters and creating the distinctive angled look of a hip roof. Jack rafters are connected to the hip rafters with precise cuts and angles, ensuring the roof’s structural integrity.
Common Rafters: The Backbone of Roof Surfaces
While jack rafters define the hip, common rafters are the backbone of the roof’s remaining surfaces. They run parallel to each other, extending from the ridge board to the eaves, supporting the roof sheathing and underlayment. Common rafters are installed with precise spacing, ensuring the even distribution of weight and avoiding any sagging or buckling.
The Connection Between Jack and Common Rafters
Jack and common rafters are linked together like puzzle pieces, forming a cohesive roof structure. Jack rafters connect to the hip rafters, which in turn connect to the ridge board. Common rafters extend from the ridge board, interlocking with the jack rafters at the hip. This intricate web of connections ensures that each rafter supports the others, creating a sturdy and reliable roof system.
Roof Framing Components: The Building Blocks of a Sturdy Roof
Every sturdy roof stands tall on the shoulders of its robust components. Let’s delve into two crucial elements: gable ends and framing squares, which play a pivotal role in ensuring the structural integrity of your roof.
Gable Ends: The Guardians of Roof Stability
Gable ends, the triangular sections that frame the edges of a roof, are more than just aesthetic enhancers. They provide essential support to the roof structure, preventing it from collapsing under external forces like wind and snow loads. When constructing gable ends, proper framing techniques are paramount to ensure their structural stability.
Framing Squares: Precision Tools for Roof Layout
Framing squares are indispensable tools for accurate roof framing. These devices help builders lay out rafters, determine angles, and ensure that the roof structure is perfectly aligned. Their precise measurements are critical for creating a well-balanced and structurally sound roof.
In gable end framing, framing squares play a crucial role in determining the correct angles for the rafters, ensuring they fit snugly against the gable ends. This precise alignment distributes weight evenly throughout the roof, reducing the risk of structural failures.
By understanding the significance and proper use of gable ends and framing squares, you can contribute to the longevity and stability of your roof. These components form the foundation upon which a sturdy and protective roof is built.
Roof Covering: The Armor of Your Abode
Roof Sheathing: The Foundation of Roofing
The roof sheathing acts as the solid base upon which your roofing rests. Crafted from various materials like plywood, oriented strand board (OSB), or wooden planks, it provides a secure platform for the underlayment and roofing to adhere to. Proper installation is crucial, ensuring a sturdy foundation for the entire roofing system.
Underlayment: The Shield Against Elements
Underlayment is the unsung hero of roofing. This thin layer serves as a barrier against moisture and wind infiltration. Constructed from waterproof materials like tar paper or synthetic membranes, it protects the roof sheathing and prevents water damage. Its precise installation is essential, ensuring a tight seal between the underlayment, roof sheathing, and roofing.
Roofing: The Crown of Your Castle
The roofing is the crown of your home, shielding it from the elements. A wide array of materials are available, including asphalt shingles, metal roofing, and tile roofing. Each material offers unique properties, such as durability, weather resistance, and aesthetics. Expert installation is paramount, ensuring a watertight seal and long-lasting protection.