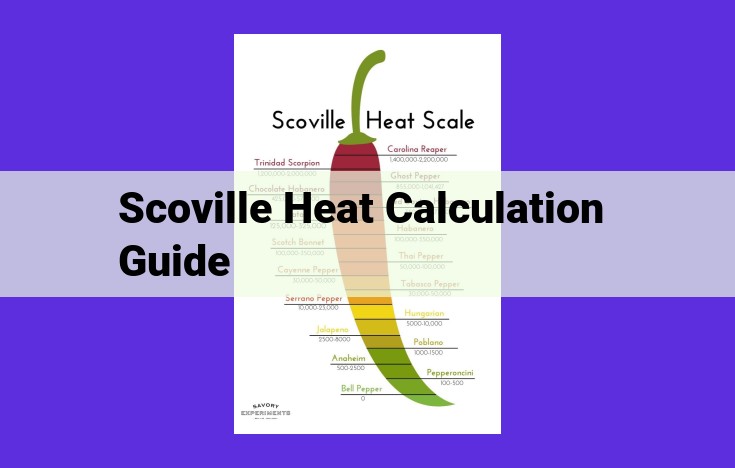
The Scoville Heat Calculation Guide is a comprehensive resource for understanding the science behind pepper heat measurement. It defines Scoville Heat Units (SHU) as a measure of capsaicin concentration, the chemical responsible for heat sensation. The guide explores related concepts like Heat Index and HPLC, techniques used to quantify capsaicin levels and estimate perceived heat. It also covers the role of Sensory Panels in subjectively evaluating heat intensity. This guide provides a solid foundation for interpreting and utilizing heat measurements, empowering individuals to navigate the world of spicy peppers with confidence.
Scoville Heat Calculation Guide: Unveiling the Fiery Secrets of Peppers
The Scoville Heat Units (SHU) is a key metric in the world of peppers, providing a precise measurement of their fiery intensity. Understanding SHU empowers us to navigate the diverse heat spectrum of peppers, from mild to scorching.
Delving into the Basics:
SHU is a standardized unit that quantifies the concentration of capsaicin, a chemical compound responsible for the fiery sensation we experience when consuming peppers. The higher the SHU, the hotter the pepper. This knowledge equips us to make informed choices when navigating the heat spectrum, whether it’s for culinary adventures, salsa making, or simply satisfying our curiosity about the world’s hottest peppers.
Scoville Heat Units: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to measuring the fiery intensity of peppers, Scoville Heat Units (SHU) take center stage. These units are essential for understanding the heat level of different peppers and navigating the world of spicy cuisine.
What are Scoville Heat Units?
SHU is a quantitative measure that calculates the amount of capsaicin in a pepper. Capsaicin is the chemical compound responsible for that spicy sensation we experience when biting into a pepper. The higher the SHU, the more capsaicin is present, and the hotter the pepper.
Related Concepts:
- Capsaicin: Capsaicin binds to receptors on our tongues, triggering the sensation of heat.
- Heat Index: A similar measure to SHU, but it estimates perceived heat based on capsaicin concentration.
- HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography): A laboratory technique that accurately determines capsaicin concentration and SHU.
Capsaicin: The Fiery Essence of Peppers
At the heart of every sizzling pepper lies a potent compound called capsaicin. This molecule is the maestro of heat, responsible for the fiery sensation that sets our mouths ablaze and leaves us reaching for the nearest glass of milk.
Properties and Effects of Capsaicin
Capsaicin is a naturally occurring chemical that binds to a specific receptor on our tongue known as the TRPV1 receptor. When capsaicin encounters this receptor, it triggers a chain reaction that sends pain signals to our brain. This is why we perceive peppers as being hot or spicy.
The intensity of the heat depends on the concentration of capsaicin in the pepper. The higher the concentration, the more receptors are activated, and the more intense the burning sensation.
Correlation between Capsaicin Concentration and SHU
The Scoville Heat Unit (SHU) is the standard measurement used to quantify the heat level of peppers. It’s a direct reflection of the capsaicin concentration. The higher the SHU value, the more capsaicin is present, and the hotter the pepper.
Related Concepts
- Scoville Heat Units (SHU): A measure of capsaicin content, directly related to heat intensity.
- Heat Index: An estimate of perceived heat based on capsaicin concentration.
- HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography): A technique used to determine capsaicin concentration and, subsequently, SHU.
Concept: Heat Index
Diving deeper into the fascinating world of pepper heat, let’s explore the intriguing concept of Heat Index. This index serves as an instrumental tool in estimating the perceived intensity of a pepper’s heat.
At its core, the Heat Index is a calculated value derived from capsaicin concentration. Capsaicin, the fiery molecule responsible for the burn of peppers, acts as the fundamental substance upon which both Heat Index and SHU (Scoville Heat Units) are based.
To ascertain the Heat Index, scientists employ a precise formula that translates capsaicin concentration into a numerical value. This value represents an estimated perception of heat, allowing us to gauge the anticipated intensity of a pepper’s spiciness.
It’s crucial to note that Heat Index and SHU, though related, are distinct measures. While SHU provides an objective measure of capsaicin content, Heat Index offers an estimated perception of heat.
To further refine our understanding of pepper heat, Sensory Panels play a vital role. These panels consist of trained individuals who subjectively evaluate the heat intensity of peppers. Their assessments complement Heat Index determinations, providing valuable insights into the perceived heat experience.
By combining the precision of Heat Index calculations with the subjective assessments of Sensory Panels, we gain a comprehensive understanding of pepper heat. This knowledge empowers us to make informed choices when selecting peppers for our culinary adventures, ensuring a harmonious balance of flavor and spice.
HPLC: Unraveling the Heat of Peppers
In the captivating realm of culinary arts, understanding the heat intensity of peppers is key to crafting mouthwatering and tantalizing dishes. Enter High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), a scientific wizard that empowers us to decipher the fiery secrets hidden within these piquant gems.
HPLC, a sophisticated analytical technique, takes the stage as the maestro of capsaicin analysis. Capsaicin, the enigmatic molecule responsible for pepper’s fiery bite, holds the key to unraveling the Scoville Heat Units (SHU). HPLC, with its unparalleled precision, measures capsaicin’s concentration, providing a direct estimate of a pepper’s heat intensity.
The process begins with a meticulous extraction of capsaicin from the pepper sample. This precious extract embarks on a journey through the HPLC’s intricate column, where it encounters a carefully calibrated solvent system. As the solvent gently propels the capsaicin along, its unique chemical properties cause it to interact with the column’s stationary phase.
Like a celestial dance, the capsaicin molecules waltz through the column, their progress meticulously monitored by a sensitive detector. The detector captures the subtle signals emitted by each capsaicin molecule, translating them into a quantifiable electrical response.
This electrical signal, a symphony of data, is then analyzed by sophisticated software. The software interprets the signal, revealing the concentration of capsaicin in the sample. Armed with this crucial information, scientists can precisely calculate the pepper’s SHU, providing an accurate measure of its fiery potential.
HPLC’s precision and accuracy make it an indispensable tool for various applications. From ensuring product consistency to advancing scientific research, HPLC empowers us to unlock the secrets of pepper heat, enabling us to craft culinary experiences that ignite taste buds and leave a lasting impression.
**The Role of Sensory Panels in Evaluating Pepper Heat**
Pepper enthusiasts and culinary professionals alike rely on the Scoville Heat Scale to gauge the intensity of peppers. While laboratory techniques provide precise measurements of capsaicin concentration, sensory panels offer a valuable subjective perspective on perceived heat.
Sensory Panels: Unveiling the Subjective Experience
Sensory panels consist of trained individuals who assess the heat intensity of peppers through taste testing. Panelists undergo rigorous training to calibrate their palates and ensure consistency in their evaluations. They rate the heat level on a standardized scale, providing valuable insights into the perceived heat experience.
Complementing Objective Measures
Sensory panels complement the objective Scoville Heat Units (SHU) and Heat Index measures. While SHU quantifies capsaicin content and Heat Index estimates perceived heat based on capsaicin concentration, sensory panels provide qualitative data that reflects the actual sensory experience.
Perception and Variability
Capsaicin, the compound responsible for pepper heat, activates receptors on the tongue, triggering a sensation of burning. The perceived heat intensity can vary depending on individual sensitivity, cultural background, and food context. Sensory panels account for these subjective factors and offer a more comprehensive understanding of pepper heat.
Reliable and Consistent Evaluations
Panelists undergo extensive training and calibration to ensure reliable and consistent results. They follow standardized protocols and use controlled testing conditions to minimize bias and subjectivity. By combining sensory evaluations with laboratory measurements, researchers and producers gain a more accurate picture of pepper heat intensity.
Sensory panels play a crucial role in understanding the subjective experience of pepper heat. By providing qualitative assessments that complement objective measures, they enhance our perception of pepper intensity and contribute to a well-rounded understanding of the spicy world. Whether you’re a pepper aficionado or simply enjoy the occasional spicy dish, sensory panels ensure that we can appreciate the full spectrum of pepper heat with confidence and accuracy.