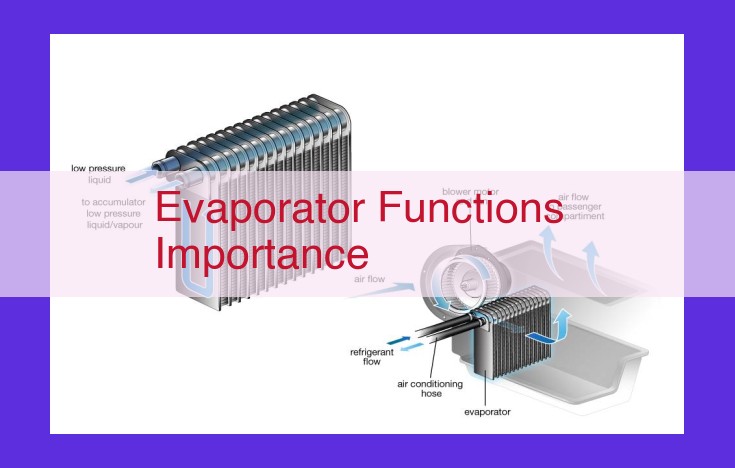
Evaporators, vital components in refrigeration systems and heat pumps, absorb heat from a cold space and facilitate the conversion of liquid refrigerant into vapor. This process extracts heat from the cold space, creating a cooling effect. The produced refrigerant vapor then circulates through the system, enabling efficient heat transfer and cooling performance. Evaporators play a crucial role in maintaining cold temperatures in cold storage spaces, ensuring food preservation and product quality.
Unveiling the Heart of Cooling and Heating: The Evaporator
Embarking on a Chilling Journey
In a realm of refrigeration and warmth, there lies a crucial component that orchestrates our comfort and preserves the freshness of our food – the evaporator. An evaporator is the maestro of heat absorption, the magician that transforms chilly spaces into cozy havens. It’s like the unsung hero working behind the scenes, keeping our world delightfully cool or invitingly warm.
The Maestro of Heat Absorption
An evaporator’s primary role is to absorb heat from its surroundings, like a sponge soaking up water from a puddle. This heat transfer is a fundamental process in both refrigeration systems and heat pumps. In refrigeration systems, the evaporator cools a designated space, such as a refrigerator or freezer, by absorbing heat from its contents. In heat pumps, the evaporator extracts heat from the outside environment, granting us toasty warmth during the cold winter months.
A Symphony of Liquid to Vapor
Within the evaporator’s icy embrace, a remarkable transformation occurs. As heat flows into the evaporator, the refrigerant inside undergoes a phase change from a liquid to a vapor. This vaporous refrigerant then carries the absorbed heat away, leaving behind a cooled space. It’s as if the evaporator orchestrates a symphony of heat absorption and vapor formation, a harmonious dance that results in refreshing coolness or comforting warmth.
Functions of an Evaporator: The Heart of Cooling and Heating Systems
In the realm of refrigeration and heat pumps, the evaporator stands as a crucial component, orchestrating the intricate dance of heat transfer. Understanding its functions is akin to unlocking the secrets of these systems’ ability to cool and heat our environments.
Heat Absorption: Cooling the Cold Space
The evaporator plays a pivotal role in absorbing heat from the cold space, the area that requires cooling. Through a process known as convection, heat from the cold space is transferred to the refrigerant flowing through the evaporator coils. This heat exchange lowers the temperature of the cold space, creating the desired cooling effect.
Vapor Formation: Creating the Refrigerant’s Gaseous Form
As the refrigerant absorbs heat, it undergoes a remarkable transformation from a liquid to a vapor state. This phase change, known as vaporization, is essential for the refrigeration process. The vaporized refrigerant, now carrying the absorbed heat, is ready to be transported to the next stage of the system for further cooling or heating.
Understanding the Evaporator: A Fundamental Component in Cooling and Heating Systems
An evaporator plays a vital role in refrigeration systems and heat pumps by efficiently absorbing heat and converting liquid refrigerant into vapor. This process forms the cornerstone of cooling and heating mechanisms, ensuring the preservation of food, beverages, and other temperature-sensitive items.
Refrigeration System
In a refrigeration system, the evaporator is responsible for cooling the cold space. When refrigerant enters the evaporator as a liquid, it absorbs heat from the cold space, causing the refrigerant to evaporate into vapor. This vapor then travels to the compressor, where it is compressed and sent to the condenser for heat release.
Heat Pump
In a heat pump, the evaporator operates differently. It absorbs heat from the outside environment instead of a cold space. This heat is then transferred to the inside of the building, providing heating during colder months.
Cold Storage Space
The evaporator’s ability to maintain cold temperatures makes it crucial for cold storage spaces such as refrigerators, freezers, and walk-in coolers. By continuously absorbing heat from the interior, the evaporator ensures food preservation and optimal product quality.
Vapor
The refrigerant vapor produced by the evaporator is a key component in the cooling and heating processes. Its low temperature enables efficient heat transfer, while its high-pressure helps drive the system.
Importance of the Evaporator
The evaporator is an essential component in both refrigeration systems and heat pumps. It facilitates efficient heat transfer, cooling performance, and overall energy efficiency of these systems. Its role is fundamental to maintaining desired temperatures and ensuring the reliability of these critical appliances.
**The Importance of an Evaporator: The Heart of Efficient Cooling and Heating**
An evaporator is a crucial component in both refrigeration systems and heat pumps, playing a pivotal role in maintaining the desired temperature in our homes and businesses. Its functions are essential for creating a comfortable and efficient environment.
Efficient Heat Transfer and Cooling Performance
The evaporator performs the critical task of transferring heat from the cold space, such as a refrigerator or a room, to the refrigerant. This heat transfer is achieved through a process called evaporation, where the refrigerant absorbs heat and changes from a liquid to a vapor. The vaporized refrigerant then carries the heat away, allowing the cold space to cool down.
Energy Efficiency and System Reliability
The evaporator’s efficiency is paramount for the overall performance of the cooling or heating system. An efficient evaporator ensures that the refrigerant absorbs the maximum amount of heat possible, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs. Additionally, a properly functioning evaporator contributes to the reliability of the system by preventing breakdowns and prolonging its lifespan.
In conclusion, the evaporator is the heart of any refrigeration or heat pump system. Its functions of heat absorption and vapor formation are essential for maintaining a desired temperature. The efficiency and reliability of the evaporator directly impact the energy consumption and performance of the system, making it a crucial component in creating a comfortable and sustainable environment.