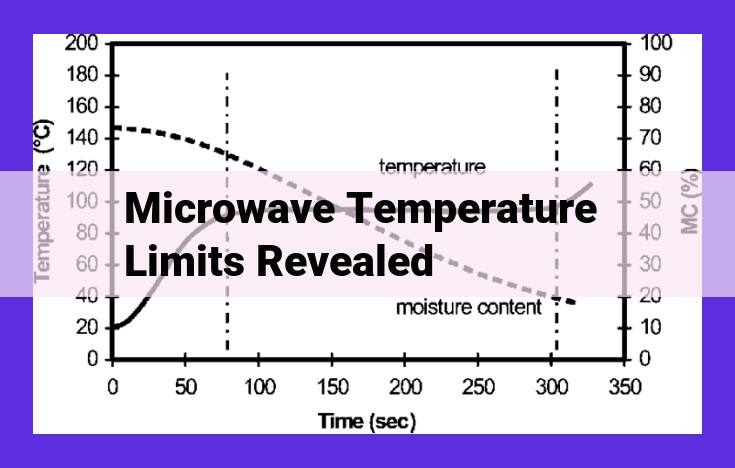
Microwave temperature limits unveil the crucial aspects of temperature distribution during microwave heating. Understanding the expected temperature profile, determining the maximum cooking temperature, ensuring the minimum cooking temperature, and optimizing temperature distribution through control of thermal penetration depth and heating rate are key to microwave cooking. Furthermore, selecting and using appropriate microwavable packaging ensures food safety and efficiency, revealing the intricate interplay between microwave heating parameters and food temperature management.
Understanding the Expected Temperature Profile in Microwave Heating
When cooking with a microwave, understanding the temperature distribution within your food is crucial. Microwave heating is a unique method that generates heat through the interaction of electromagnetic waves with food molecules. This energy absorption creates a distinctive temperature profile that differs from traditional cooking methods.
The thermal penetration depth determines how deeply microwaves penetrate into the food. It is influenced by factors like the microwave frequency, the food’s density, and its moisture content. The higher the penetration depth, the more evenly the heat is distributed.
Heating rate is another factor that affects the temperature profile. Faster heating rates result in more uniform heat distribution, reducing cold spots and overcooked areas. However, extremely rapid heating can cause uneven cooking and potential safety hazards. Finding the optimal heating rate is essential for ensuring thorough cooking without compromising safety.
Determining the Maximum Cooking Temperature
In the realm of microwave cooking, understanding the maximum cooking temperature is paramount. It plays a crucial role in ensuring food safety and maintaining optimal temperature distribution throughout your culinary creations.
The maximum cooking temperature refers to the highest internal temperature that a food item should attain to eliminate harmful microorganisms and guarantee its safety for consumption. Exceeding this temperature can lead to uneven heating, overcooking, and potential loss of nutrients.
Furthermore, the maximum cooking temperature is intrinsically linked to the minimum cooking temperature. It’s a delicate balancing act, where the desired doneness level must be achieved while adhering to food safety guidelines. In general, the higher the maximum cooking temperature, the lower the minimum cooking temperature required to ensure food safety.
For instance, cooking chicken to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) is crucial to eliminate harmful bacteria, such as Salmonella. This relatively high maximum cooking temperature allows for greater flexibility in cooking methods and doneness levels. On the other hand, cooking fish to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C) requires a lower maximum cooking temperature to prevent overcooking and ensure a moist, tender texture.
Understanding the maximum cooking temperature and its relationship with the minimum cooking temperature is essential for successful microwave cooking. By adhering to these guidelines, you can ensure safe, evenly cooked dishes that delight your taste buds and safeguard your well-being.
Ensuring Minimum Cooking Temperature
- Discuss the importance of minimum cooking temperature for food safety.
- Describe factors that determine minimum cooking temperature, including food type and safety guidelines.
Ensuring Minimum Cooking Temperature for Food Safety
Maintaining a minimum cooking temperature is crucial for food safety. It ensures that harmful bacteria and microorganisms are eliminated, preventing foodborne illnesses. The minimum cooking temperature varies depending on the type of food and is established by safety guidelines.
One of the primary factors influencing minimum cooking temperature is the food’s composition. Meats, such as poultry, beef, and pork, require higher temperatures to eliminate potential pathogens like Salmonella and E. coli. Fish also has specific minimum cooking temperatures to prevent the growth of bacteria like Listeria monocytogenes.
In addition to the food type, cooking methods can impact the required minimum temperature. For example, microwave cooking requires higher temperatures than conventional ovens to achieve the same level of safety. This is because microwaves heat food unevenly, creating hot and cold spots.
By understanding the minimum cooking temperatures for different foods, consumers can help ensure their safety. Food thermometers are a valuable tool for accurately measuring internal food temperatures. Inserting a thermometer into the thickest part of the food and ensuring it reaches or exceeds the recommended minimum temperature is vital.
Remember, food safety should be a top priority. By following safety guidelines and ensuring minimum cooking temperatures are met, individuals can minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses and enjoy safe and delicious meals.
Optimizing Temperature Distribution for Perfect Microwave Cooking
When it comes to microwave cooking, achieving an even temperature distribution is crucial for ensuring both food safety and culinary delight. Temperature distribution refers to how heat spreads throughout the food, affecting its overall quality and doneness.
Factors Influencing Temperature Distribution:
Several factors impact temperature distribution in microwaved food:
- Thermal Penetration Depth: This determines how far microwaves penetrate into the food, influencing the heat distribution within. Microwaves have a limited penetration depth, and thicker foods may have uneven heating.
- Heating Rate: The speed at which the microwaves heat the food affects temperature distribution. A higher heating rate can lead to uneven heating, while a slower heating rate allows for more uniform cooking.
Effects of Uneven Temperature Distribution:
Uneven temperature distribution can compromise food safety and enjoyment:
- Undercooked Areas: Spots with insufficient heat may harbor harmful bacteria, posing health risks.
- Overcooked Areas: Portions exposed to excessive heat can become dry, tough, or even burn, detracting from the food’s taste and texture.
Strategies for Optimizing Temperature Distribution:
To ensure optimal temperature distribution in microwaved food, try these techniques:
- Stir or Rotate Food: Periodically stirring or rotating the food allows microwaves to reach different areas, promoting even heating.
- Use a Turntable: Microwaves with turntables ensure the food is exposed to microwaves from various angles, fostering uniform heating.
- Cover Food: Covering food loosely with a microwave-safe lid traps the steam and allows heat to circulate within the container. This helps distribute temperature evenly throughout the food.
- Choose the Right Cookware: Microwavable containers made of materials like ceramic or glass can withstand heat and allow microwaves to penetrate better, resulting in more uniform cooking.
- Cook in Smaller Batches: Microwaving large amounts of food can lead to uneven heating. To ensure even distribution, cook in smaller batches or cut the food into smaller pieces.
By following these tips, you can optimize temperature distribution in your microwaved food, ensuring both food safety and mouthwatering results every time.
Understanding Thermal Penetration Depth: A Crucial Factor in Microwave Heating
What is Thermal Penetration Depth?
When microwaves encounter food, their energy gets absorbed and converted into heat. However, this heat does not penetrate uniformly throughout the food. Instead, it penetrates only a certain distance known as the thermal penetration depth. This depth plays a vital role in ensuring even cooking and food safety.
Factors Affecting Thermal Penetration Depth
The thermal penetration depth is influenced by several factors:
-
Food properties: The density, thickness, and moisture content of food affect how well microwaves penetrate. Denser and thicker foods have a smaller penetration depth, while foods with higher moisture content allow microwaves to penetrate deeper.
-
Microwave frequency: Higher frequency microwaves have a shallower penetration depth than lower frequency microwaves. This is because higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths, which are more easily absorbed by food molecules.
Significance of Thermal Penetration Depth
The thermal penetration depth has crucial implications for microwave cooking:
-
Uniform cooking: Microwaves tend to heat the surface of food more quickly than the interior. Understanding the thermal penetration depth helps determine the appropriate cooking time and power to ensure uniform heating.
-
Food safety: Microwaves are effective in killing bacteria if the internal temperature of the food reaches safe levels. The thermal penetration depth helps ensure that sufficient heat penetrates the food to inactivate harmful microorganisms.
-
Optimizing energy consumption: Microwaving food for longer than necessary wastes energy. By understanding the thermal penetration depth, you can cook food efficiently without overcooking or extending cooking times.
By understanding the concept of thermal penetration depth and its contributing factors, you can optimize microwave cooking for safe, even, and energy-efficient results.
Controlling Microwave Heating Rate: The Key to Efficient and Safe Cooking
When it comes to microwave cooking, time is everything. Controlling the heating rate is crucial for achieving evenly cooked and safe food. Understanding the factors that determine heating rate can help you master the art of microwave cooking.
Microwave Power
The power of your microwave oven plays a significant role in heating rate. Higher power levels generate more microwaves, resulting in a faster heating process. Conversely, lower power levels heat food more gradually.
Food Mass
The amount of food being cooked also affects heating rate. Larger quantities of food require more time to heat evenly because microwaves penetrate deeper into the food. As a result, it’s essential to adjust the heating time and power level accordingly.
Microwave Frequency
Microwaves operate at a specific frequency, typically 2.45 GHz. This frequency determines the penetration depth of the microwaves into the food. Foods with high moisture content, such as fruits and vegetables, allow microwaves to penetrate deeper and heat more quickly.
Tips for Optimal Heating Rate
- Start with a lower power level and gradually increase it as needed to prevent overcooking.
- Cook smaller portions to ensure even heating.
- Stir or rearrange food during cooking to promote uniform heating.
- Use a microwavable cover to trap heat and reduce cooking time.
- Be mindful of food density and adjust heating time accordingly. Dense foods, like meat, require longer cooking periods.
By mastering the microwave heating rate, you can unlock the full potential of your microwave oven. Enjoy safe, evenly cooked meals with ease and efficiency.
Selecting and Using Microwavable Packaging: A Culinary Safety Guide
Microwaving, a convenient and time-saving cooking method, has become a kitchen staple. However, selecting the right microwavable packaging is crucial for safety and food quality.
Purpose of Microwavable Packaging
Microwavable packaging serves several essential purposes:
- Prevents splattering: It protects your microwave and food from splatters and messes.
- Promotes even cooking: It helps distribute heat evenly, ensuring your food cooks thoroughly.
- Maintains moisture: It traps steam, keeping your food moist and juicy.
Safety Considerations
When choosing microwavable packaging, safety should be paramount:
- Microwave-safe materials: Only use packaging specifically labeled as microwave-safe. Non-microwave-safe materials can melt, leak, or even explode when heated.
- Avoid metal: Metal can reflect microwave waves, creating hot spots and potentially causing sparks or fire.
- Choose BPA-free containers: Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical linked to health concerns. Opt for BPA-free packaging to protect your food.
Types of Microwavable Materials
Various microwavable materials are available, each with its advantages and uses:
- Plastic containers: Durable and dishwasher-safe, plastic containers are suitable for reheating leftovers or cooking small meals.
- Paper bags: Convenient and disposable, paper bags are ideal for popcorn, vegetables, and other foods that require air circulation.
- Silicone: Flexible and heat-resistant, silicone steaming bags are perfect for vegetables, fish, and other delicate dishes.
- Glass: Non-porous and easy to clean, glass containers can be used for a wide range of foods, including sauces, soups, and reheating meals.
Choosing the Right Packaging
Matching the packaging to the food you’re microwaving is essential:
- Dense foods: Use plastic containers or glassware that can withstand high temperatures.
- Delicate foods: Opt for silicone bags or paper bags that allow for gentle steaming.
- Liquids: Choose containers with secure lids to prevent spilling and splattering.
Tips for Safe Microwave Cooking
- Remove excess packaging: Discard any unnecessary packaging and only keep what is necessary.
- Do not use foil or Styrofoam: These materials are not microwave-safe and can be hazardous.
- Monitor cooking time: Check the food regularly to ensure it is cooked thoroughly but not overcooked.
- Let it rest: Allow the food to rest for a few minutes after microwaving to distribute the heat evenly.
Microwavable packaging is essential for safe and convenient microwave cooking. By understanding its purpose, safety considerations, and types available, you can make informed choices that ensure your food is heated evenly, safely, and enjoyably.