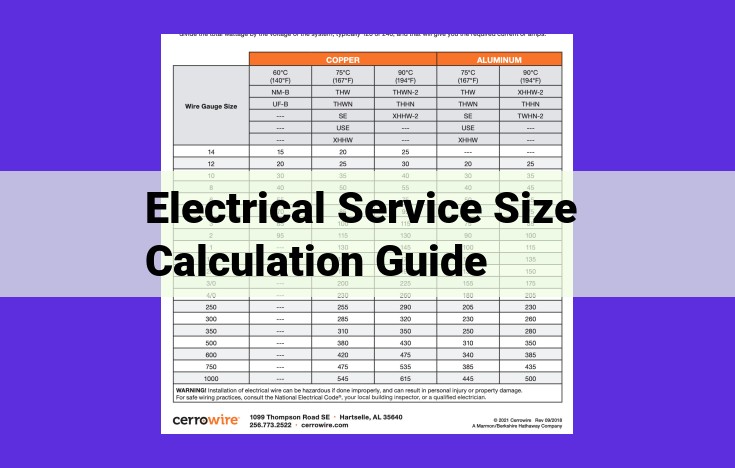
- Electrical service size calculation guide provides instructions for determining the appropriate electrical service size for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
- It covers load calculation, service entrance, circuit breakers and fuses, electrical panel, voltage drop, grounding, and electrical code requirements.
- Proper electrical service size calculation ensures safety and efficiency, prevents overloading, and meets code specifications.
Calculating Electrical Service Size: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of electricity, understanding the size of your electrical service is paramount to ensuring a safe, efficient, and code-compliant power distribution system. Whether you’re planning a residential renovation, starting a commercial enterprise, or managing an industrial facility, calculating the appropriate electrical service size is critical.
Importance of Electrical Service Size Calculation
Ignorance or miscalculation of electrical service size can lead to numerous hazards:
- Electrical Fires: Overloaded circuits due to insufficient capacity can spark disastrous fires.
- Power Outages: Undersized service fails to meet the electrical demands, resulting in frequent power outages.
- Equipment Damage: Excessive voltage fluctuations and brownouts can damage sensitive appliances and equipment.
- Inefficiency: Improper sizing wastes energy, leading to higher utility bills.
- Code Violations: Failure to comply with electrical codes can incur fines and safety risks.
Understanding Different Applications
The type of application—residential, commercial, or industrial—dictates the specific requirements for electrical service size.
- Residential: Homes typically require lower electrical loads for lighting, appliances, and electronics.
- Commercial: Businesses have varying electrical demands based on the nature of their operations, from retail stores to offices to restaurants.
- Industrial: Factories and manufacturing plants necessitate high-capacity electrical service to power heavy machinery and complex production processes.
Residential Electrical Service Size: Ensuring Safe and Efficient Power Distribution
In the realm of homeownership, understanding the intricacies of your electrical system is paramount for ensuring safety, comfort, and efficiency. A crucial aspect of this is determining the appropriate electrical service size for your residence.
Components of Residential Electrical Service
The core components of a residential electrical service include the electrical panel, circuit breakers or fuses, wire size, and conduit size. The electrical panel acts as the central distribution hub for electricity throughout the home, while circuit breakers or fuses protect the circuits from overloads. Wire size and conduit size determine the capacity and safety of the wiring system.
Factors to Consider
When calculating the electrical service size for your home, several factors need to be taken into account:
-
Electrical Load: This refers to the total amount of electricity consumed by all appliances and devices in the house. It’s important to consider both present and future electrical needs.
-
Demand Factor: Appliances and devices don’t always operate simultaneously. The demand factor accounts for this by estimating the percentage of the total electrical load that is likely to be used at any given time.
-
Power Factor: This factor represents the efficiency of power utilization. A higher power factor indicates that less energy is lost to inefficiency, allowing for a smaller electrical service size.
Determining the Service Size
The specific electrical service size required for your home depends on these factors. A licensed electrician can assess your electrical load, demand factor, and power factor to provide an accurate calculation. In general, a typical residential service size ranges from 100 to 200 amps.
Balancing Safety and Efficiency
It’s crucial to balance safety and efficiency when calculating your electrical service size. An undersized service can lead to overloads and potential fire hazards, while an oversized service can be costly and inefficient. By understanding the factors involved and working with a qualified electrician, you can ensure that your home’s electrical system meets your needs while complying with all safety regulations.
Commercial Electrical Service Size: Powering Your Business’s Productivity
Commercial establishments demand a reliable and efficient electrical service to support their day-to-day operations. The size of this service, measured in amps, is crucial for ensuring that all electrical equipment and systems function seamlessly, without overloading or causing power outages.
Unlike residential electrical service, which typically handles smaller loads, commercial establishments require larger capacity electrical panels and circuit breakers/fuses. These components are designed to handle the higher electrical demand associated with commercial activities, such as lighting, heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and specialized machinery.
Two key factors that influence the size of a commercial electrical service are demand factor and power factor. Demand factor is the ratio of the maximum demand for electricity over a specified period to the total connected load. It accounts for the fact that not all equipment operates at the same time or at full capacity. Power factor is a measure of the efficiency of power utilization. A lower power factor means that more current is required to transmit the same amount of power, which can lead to higher energy consumption and reduced efficiency.
Key Considerations for Commercial Electrical Service Size
- Total connected load: Determine the total wattage of all electrical equipment and systems in the commercial space.
- Demand factor: Estimate the average and peak demand for electricity based on the usage patterns and operating hours of the establishment.
- Power factor: Evaluate the types of equipment used and implement power factor correction measures to improve efficiency.
- Electrical panel capacity: Select an electrical panel with a rating that exceeds the total calculated load, including the demand factor.
- Circuit breaker/fuse ratings: Ensure that circuit breakers and fuses are sized appropriately for the wire size and connected load.
- Compliance with electrical codes: Adhere to local electrical codes and standards to ensure safety and minimize potential hazards.
By carefully considering these factors and consulting with qualified electricians, commercial establishments can ensure that their electrical service size is adequate to meet their operational needs, while maintaining safety and efficiency. This will optimize energy consumption, minimize downtime, and contribute to the smooth and uninterrupted functioning of the business.
Industrial Electrical Service Size: Powering the Heavyweights of Industry
When it comes to industrial facilities, electrical service size takes on a whole new level of importance and complexity. These colossal powerhouses demand a tailored approach to ensure their energy needs are met safely and efficiently.
Capacity and Complexity: A League of Its Own
Industrial operations often require immense amounts of electricity to fuel their machinery, equipment, and lighting systems. The electrical service size must be carefully calculated to accommodate these high energy demands. Unlike residential or commercial applications, industrial settings feature larger capacity electrical panels, circuit breakers, and fuses.
Demand Factor and Power Factor: Critical Considerations
In industrial settings, it’s crucial to account for demand factor and power factor when determining service size. Demand factor represents the percentage of simultaneous usage of appliances or equipment, while power factor measures the efficiency of power utilization. Understanding these factors is vital for optimizing electrical system performance and minimizing energy waste.
The Role of Load Calculation
Calculating the electrical load of an industrial facility is a meticulous process that involves considering all connected devices and appliances. This calculation helps determine the total electrical load, ensuring that the electrical service size can adequately handle the combined power requirements.
Industrial electrical service size plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of these energy-intensive facilities. By carefully considering the required capacity, demand factor, power factor, and load calculation, industrial professionals can optimize their electrical systems to meet the unique demands of their operations. Compliance with electrical codes and consulting with qualified electricians remain essential for maintaining a safe and reliable electrical environment.
Calculating Electrical Service Size: A Guide to Efficient Home Power
Ensuring a safe and efficient electrical system for your home begins with calculating the appropriate electrical service size. This involves determining the total electrical load, accounting for simultaneous appliance usage, and considering the efficiency of power utilization.
Determining the Total Electrical Load
The total electrical load of your home represents the sum of the power requirements of all appliances and devices. To calculate this, you’ll need to list all the appliances and their wattage ratings. Don’t forget to include lighting, HVAC systems, and any other electrical equipment.
Accounting for Simultaneous Appliance Usage (Demand Factor)
While unlikely that all appliances will operate simultaneously, it’s essential to account for their demand factor. This factor represents the percentage of the total load that is expected to be used at any given time. Typically, residential buildings have a demand factor of 0.8 to 1.0.
Considering Power Factor
The power factor measures the efficiency of your electrical system. It’s the ratio of real power (power used by appliances) to apparent power (total power drawn from the source). A low power factor indicates that your system is consuming more energy than it needs. This can lead to increased energy costs and reduced system efficiency.
Calculating electrical service size requires careful consideration of these factors. By understanding the total load, demand factor, and power factor, you can ensure your home has an electrical system that meets its power needs, promotes efficiency, and complies with electrical codes.
**The Service Entrance: The Gateway to Your Electrical System**
The service entrance is the entry point for electrical service into your building. It’s the junction where the power from the utility company connects to your internal electrical system. This vital component ensures the safe and efficient distribution of electricity throughout your property.
At the service entrance, the incoming power typically passes through a circuit breaker or fuse, which serves as a protective barrier. These devices are designed to trip or blow in the event of an electrical fault, preventing damage to your wiring and appliances.
From the service entrance, the power is distributed to the electrical panel, which is the central hub of your electrical system. The panel houses circuit breakers or fuses that control the electrical circuits in your building. Each circuit is dedicated to a specific area or appliance, providing localized protection and allowing for easy isolation in case of issues.
When selecting the size and capacity of your service entrance, it’s crucial to consult with a qualified electrician. They will assess your electrical needs, consider the demand factor (simultaneous usage of appliances), and determine the appropriate wire size and conduit size to minimize voltage drop and ensure the safe and efficient operation of your electrical system.
Circuit Breakers and Fuses: The Protectors of Your Electrical System
Your home’s electrical system is a complex network of wires, switches, and outlets that provide power to your appliances, lights, and other devices. Behind the scenes, there are two essential components that silently work to keep your system safe and reliable: circuit breakers and fuses.
These protective devices play a crucial role in preventing electrical fires and damage to your electrical equipment. They act as circuit guards, monitoring the flow of electricity and tripping or blowing when the current exceeds safe levels.
Matching Circuit Breakers/Fuses to Wire Size
The wire size in your electrical system determines the amount of current it can safely carry. Circuit breakers and fuses must be sized appropriately to match the wire size, ensuring that the protective device will trip or blow before the wire overheats and poses a fire hazard.
Types of Circuit Breakers and Fuses
Circuit breakers are reusable protective devices that can be reset after they have tripped. They are typically installed in electrical panels and come in different amperage ratings, each designed to protect a specific wire size.
Fuses, on the other hand, are one-time-use devices that burn out when the current exceeds their rating. They must be replaced with a new fuse of the same amperage after they have blown.
Importance of Proper Sizing
Using circuit breakers and fuses that are too large or too small can compromise the safety of your electrical system. Undersized devices may fail to trip or blow before the wire overheats, increasing the risk of a fire. Oversized devices may allow excessive current to flow, potentially damaging your electrical equipment.
Consult a Qualified Electrician
Determining the correct size of circuit breakers and fuses for your electrical system requires technical knowledge and experience. It is highly recommended to consult with a qualified electrician to ensure the safety and reliability of your electrical installation. They can assess your electrical load, wire size, and other factors to recommend the appropriate protective devices for your home.
Electrical Panel: The Heart of Your Electrical System
At the heart of every electrical system lies the electrical panel, the command center that distributes power throughout your building. This unassuming box plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safe and efficient flow of electricity to all your appliances, lighting, and devices.
The capacity of an electrical panel is measured in amps, indicating the maximum amount of current it can handle. Choosing the right capacity is crucial, as overloading the panel can lead to circuit breakers tripping or worse, electrical fires. Determining the capacity of your electrical panel involves calculating the total electrical load of your building, taking into account the simultaneous usage of appliances and the efficiency of power utilization.
Once the capacity is determined, it’s time to select the appropriate circuit breakers or fuses. These protective devices are essential for safeguarding your circuits from overloads. They trip when the current flow exceeds a safe level, preventing damage to wires and appliances. The size of the circuit breakers or fuses must match the wire size, ensuring that the wire can safely handle the current it carries.
Inside the electrical panel, conductors known as bus bars distribute power to the individual circuits. The size of the bus bars is also important, as it must be able to conduct the total current of all the circuits combined.
Don’t underestimate the importance of regular electrical panel maintenance. A qualified electrician can inspect your panel, check for loose connections, and ensure that all components are operating as intended. This proactive measure helps prevent electrical issues and ensures the safety and reliability of your electrical system.
When it comes to electrical panels, understanding their function and importance is paramount. By considering the capacity, circuit breakers, bus bars, and regular maintenance, you can ensure that this essential component of your electrical system operates seamlessly and safely, providing you with the power you need.
Understanding Voltage Drop: The Critical Factor in Electrical Service Size Calculation
Every electrical system experiences a voltage drop as electricity travels through its components. This drop in voltage is caused by the resistance of the wires, which impedes the flow of electrons. The amount of voltage drop depends on several factors, including the distance the electricity must travel, the load on the circuit, and the size of the wires.
The voltage drop is directly proportional to the resistance of the wire. This means that the smaller the wire, the greater the resistance and the higher the voltage drop. Similarly, the longer the wire, the greater the resistance and the higher the voltage drop.
The load on the circuit also affects the voltage drop. The heavier the load, the greater the current draw, and the higher the voltage drop. This is because a higher current draw requires more electrons to flow through the wire, which increases the resistance and voltage drop.
To minimize voltage drop, it’s crucial to select the appropriate wire size for the load and distance. Larger wires have lower resistance, resulting in less voltage drop. However, it’s also important to consider the cost and practicality of using larger wires, as they can be more expensive and difficult to install.
Impact of Wire Size and Conduit Size on Voltage Drop
The wire size directly influences the voltage drop. Larger wires have lower resistance and reduce voltage drop. The conduit size also plays a role, as it affects the wire’s temperature and resistance. Larger conduits allow for better heat dissipation, which keeps the wires cooler and reduces resistance.
Implications for Electrical Service Size Calculation
Voltage drop is an essential consideration in electrical service size calculation. Adequate wire sizes and conduit sizes must be selected to ensure that the voltage drop is within acceptable limits. This is critical for maintaining the safety and efficiency of the electrical system. Failing to account for voltage drop can result in overloaded circuits, which can cause fires and other hazards.
Therefore, when determining the electrical service size for a building, it’s essential to consult with a qualified electrician who can calculate the voltage drop and recommend the appropriate wire sizes and conduit sizes. This will ensure a safe and reliable electrical system that meets all applicable electrical codes.
Grounding: Ensuring Electrical Safety
Your electrical system is the lifeline of your home, providing power to all your appliances and devices. However, electricity can also be dangerous if not handled properly. Grounding plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety of your electrical system and protecting you and your family from electrical hazards.
What is Grounding?
Grounding is the process of creating a low-resistance path for electrical current to flow back to the earth. This path provides a safe escape route for stray electricity, preventing it from overloading circuits or causing shocks.
How Does Grounding Work?
Electrical systems have three main conductors: hot, neutral, and ground. Hot conductors carry the electricity to your appliances, while neutral conductors provide a path back to the power source. Ground conductors, on the other hand, are designed to handle any excess electricity that may flow through the system.
When excess electricity flows through the ground conductor, it is safely dissipated into the earth. This prevents the electricity from building up in your electrical system and causing shocks or fires.
Why is Grounding Important?
Grounding is essential for several reasons:
- Electrical Safety: Grounding protects you and your family from electrical shocks by providing a safe path for excess electricity to flow.
- Equipment Protection: Grounding also protects your electrical appliances and devices from damage caused by power surges or electrical faults.
- Compliance: Grounding is required by electrical codes to ensure the safety of your electrical system.
Installing a Grounding System
Grounding systems can be installed by qualified electricians. They typically involve:
- Installing a ground rod into the earth outside your home
- Connecting the ground rod to the electrical panel
- Running ground wires from the electrical panel to all outlets and appliances
Grounding is a vital safety measure that helps protect you, your family, and your electrical system from the dangers of electricity. By ensuring that your electrical system is properly grounded, you can enjoy a safe and efficient electrical environment in your home.
**Electrical Code: Ensuring Safety and Efficiency in Electrical Service Size Calculations**
When it comes to determining the electrical service size for your home, business, or industrial facility, adhering to the electrical code is paramount. This comprehensive set of regulations serves as the cornerstone of electrical safety and efficiency.
The electrical code establishes strict specifications for various electrical components, including the service entrance, circuit breakers/fuses, electrical panels, wire size, conduit size, and grounding. By following these specifications, you can ensure that your electrical system is properly installed and maintained, minimizing the risk of hazards such as electrical fires and shocks.
For example, the electrical code specifies the minimum wire size that can be used for a particular amperage load. This is crucial to prevent overheating and potential electrical fires. Similarly, the code dictates the appropriate circuit breaker or fuse size to match the wire size. Oversized circuit breakers or fuses can allow excessive current to flow, damaging electrical equipment or causing a fire.
Proper grounding is another critical element addressed by the electrical code. Grounding provides a safe path for stray electricity to dissipate, protecting equipment and personnel from electrical shocks. The code specifies the required grounding methods and materials, ensuring that grounding is effective and compliant.
By adhering to the electrical code, you can ensure safe and efficient power distribution in your electrical system. Compliance is not only essential for your own safety but also a legal requirement in many jurisdictions.
Therefore, it is always advisable to consult with qualified electricians who are well-versed in the electrical code. They can guide you in calculating the appropriate electrical service size and ensure that your system is installed and maintained in accordance with the code’s stringent safety and efficiency standards.