- Arc voltage regulates arc stability and penetration, while arc current affects deposition rate and penetration.
- Arc length influences heat distribution, penetration, and stability, requiring adjustment for optimal results.
- Balanced travel speed, arc length, and current optimize penetration, heat input, productivity, and weld quality.
Understanding Arc Voltage: The Key to Arc Stability and Weld Quality
In the intricate world of welding, arc voltage reigns supreme as a fundamental factor influencing the stability and quality of your welds. It’s like the conductor in an orchestra, harmonizing the flow of electrons to create a precise and consistent arc.
Arc voltage, measured in volts, plays a crucial role in determining the behavior of the electric arc. By modulating the voltage, you can fine-tune the arc characteristics, affecting its stability, energy concentration, and ultimately, the penetration and quality of your welds.
Voltage’s Impact on Arc Stability
A stable arc is the foundation of a successful weld. Arc voltage ensures that the arc remains focused and steady, preventing the dreaded “arc blow” or “arc wandering.” Proper voltage maintains a consistent distance between the electrode and the workpiece, creating an optimal environment for electron flow and weld pool formation.
Voltage’s Influence on Weld Penetration
Voltage also has a profound effect on weld penetration, the depth to which the weld metal penetrates the base metal. Higher voltages generate a more intense arc, delivering greater energy to the weld zone and resulting in deeper penetration. In contrast, lower voltages produce a shallower arc, suitable for welding thin materials or situations where excessive penetration is undesirable.
Understanding the relationship between arc voltage, arc characteristics, and penetration empowers you to optimize your welding parameters for specific applications. Whether you’re striving for deep penetration or precise surface welding, mastering arc voltage will elevate your welding skills to new heights.
The Significance of Arc Current in Welding
In the realm of welding, arc current plays a pivotal role in determining the characteristics and quality of the weld. The interplay between arc current and other welding parameters is crucial for achieving optimal results.
Influence on Weld Penetration
Arc current exerts a profound influence on the penetration depth of the weld. Higher currents enhance penetration by intensifying the heat generated at the arc point. This increased heat melts more base metal, enabling deeper welds with stronger joints.
Deposition Rate and Arc Stability
Arc current also affects the deposition rate, which refers to the amount of filler metal deposited per unit time. Higher currents accelerate the melting rate of the electrode, leading to higher deposition rates. However, excessive currents can compromise arc stability, causing spattering and inconsistent welds.
Interplay with Other Parameters
Arc current interacts with other welding parameters to achieve the desired weld properties. For instance, increasing current can compensate for lower arc voltage, maintaining arc stability and penetration. Conversely, reducing current requires higher arc voltage to sustain the arc and achieve adequate penetration.
Optimizing Arc Current
The optimal arc current depends on the type of welding process, material thickness, and desired weld characteristics. Welders must carefully adjust the current to achieve the correct balance of penetration, deposition rate, and arc stability. Too high or too low currents can lead to weld defects or subpar performance.
Arc current is a fundamental welding parameter that significantly impacts the weld quality and characteristics. By understanding the influence of arc current on weld penetration, deposition rate, and arc stability, welders can optimize their welding processes to produce high-quality welds with the desired properties.
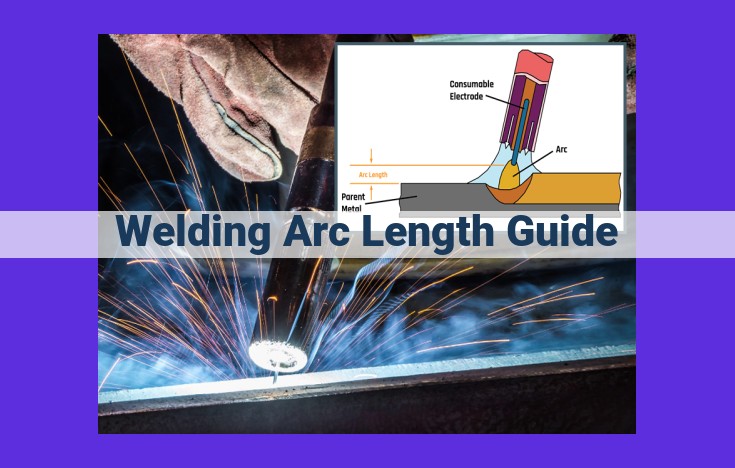
The Role of Arc Length in Welding: Striking the Optimal Balance
Every welder knows that arc length is crucial for welding success. It directly influences arc stability, heat distribution, and penetration, ultimately affecting the quality of your welds. Adjusting the arc length is an art form that can make or break your welding project.
Effect on Arc Stability and Heat Distribution
Arc length refers to the distance between the tip of the welding electrode and the workpiece. When the arc length is too long, the voltage increases, making it more difficult to maintain a stable arc. The longer the arc, the more the electrical energy is dispersed, resulting in less heat concentration at the weld joint. This can lead to shallow and weak welds.
Conversely, if the arc length is too short, the voltage drops, causing the arc to become unstable and erratic. The higher heat concentration in this case can result in excessive penetration, which can weaken the weld joint and cause distortion or burn-through.
Adjustment for Optimal Weld Characteristics
Finding the optimal arc length is essential for achieving desired weld characteristics. A well-balanced arc length ensures consistent heat distribution, resulting in welds with the correct penetration, bead shape, and strength.
To adjust the arc length, you can either move the welding torch closer to or further away from the workpiece. The ideal arc length varies depending on the welding process, material thickness, and desired weld results. It’s crucial to experiment and find the arc length that produces the best results for your specific application.
Mastering the role of arc length is a key skill for any welder. By understanding how arc length affects arc stability and heat distribution, you can optimize your welding parameters to produce high-quality, strong, and durable welds. Remember, the optimal arc length is a fine balance that requires a keen eye and a steady hand.
**Mastering Weld Penetration: A Comprehensive Guide**
Welding is a crucial skill in various industries, and achieving optimal weld penetration is paramount for ensuring the strength and quality of the finished product. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the factors that influence weld penetration and provide practical tips to optimize this vital aspect of the welding process.
Factors Influencing Weld Penetration
Weld penetration is determined by the combined effects of three key parameters:
- Arc Length: The distance between the electrode and the workpiece. Increased arc length reduces penetration, while a shorter arc length enhances it.
- Welding Current: The amount of electrical current flowing through the circuit. Higher currents provide greater penetration, but also increase heat input and can lead to overheating if not controlled.
- Travel Speed: The rate at which the welding torch moves along the joint. Faster travel speeds result in shallower penetration, while slower speeds allow for deeper penetration.
The Significance of Weld Penetration
Achieving optimal weld penetration is essential for several reasons:
- Weld Strength: Sufficient penetration creates a strong weld joint that can withstand both static and dynamic loads.
- Quality Assurance: Proper penetration ensures that the melted metal fully fuses with the base metal, creating a cohesive bond.
- Defect Prevention: Insufficient penetration can lead to defects such as porosity, lack of fusion, and undercutting, which can compromise the weld’s integrity.
Tips for Optimizing Weld Penetration
To maximize penetration and achieve superior weld quality, follow these best practices:
- Use High Welding Currents: Employing higher currents increases arc energy and enhances penetration. However, avoid excessive current, as it can cause overheating and distortion.
- Maintain a Short Arc Length: Keeping the arc length consistent and as short as possible promotes deeper penetration.
- Slow Down Travel Speed: Reducing travel speed allows the arc to dwell longer on the workpiece, resulting in greater penetration.
- Consider a Pulsed Arc: Pulsed arcs deliver energy in bursts, creating a more focused arc that improves penetration and reduces spatter.
- Utilize Filler Metal: Adding filler metal helps control penetration by adjusting the arc gap and providing additional material for the weld.
Understanding the influence of arc length, current, and travel speed on weld penetration is crucial for achieving optimal results in welding. By carefully considering these parameters and implementing the techniques outlined above, you can master the art of weld penetration and produce strong, high-quality welds every time.
Balancing Travel Speed: The Key to Achieving Desired Weld Properties
Introduction:
When it comes to arc welding, balancing travel speed is critical for achieving the desired weld quality, strength, and productivity. In this blog, we’ll explore the impact of travel speed on your welds and provide valuable considerations to help you optimize this parameter for your specific welding needs.
The Impact of Travel Speed
Travel speed significantly influences three key aspects of your welds:
- Heat Input: Higher travel speeds result in lower heat input, while slower speeds increase it. This is because the torch spends less time in any given area at higher speeds, reducing the amount of heat deposited.
- Weld Quality: Travel speed also affects weld quality. Too high a speed can lead to incomplete fusion and lack of penetration, while too low a speed can cause overheating and weld defects.
- Productivity: Naturally, travel speed plays a crucial role in productivity. Faster travel speeds allow you to complete welds in less time, increasing your efficiency.
Considerations for Optimization
To optimize travel speed for your welding application, consider the following factors:
- Joint Geometry: The thickness and shape of the joint impact the required heat input and penetration. Thicker joints may require slower travel speeds to ensure proper penetration.
- Welding Process: Different welding processes, such as MIG or TIG, have different heat input characteristics. Adjust your travel speed accordingly to match the process.
- Filler Material: The type of filler material used can also affect the optimal travel speed. Some materials, like aluminum, require higher travel speeds to prevent overheating.
- Desired Weld Properties: The desired strength, ductility, and appearance of the weld will also influence the travel speed. For critical welds, slower speeds may be necessary to achieve the required properties.
Conclusion:
Balancing travel speed is an essential aspect of arc welding. By understanding its impact on heat input, weld quality, and productivity, you can optimize this parameter to achieve the desired weld properties for your application. Remember to consider the joint geometry, welding process, filler material, and desired weld properties when determining the optimal travel speed for your welding needs.
Heat Input Considerations: The Balancing Act for Weld Quality
In the world of welding, heat input is the unsung hero that profoundly impacts the quality, strength, and durability of your welds. It’s the delicate dance of delivering the right amount of heat to the weld zone to achieve optimal results. But too much or too little heat can spell trouble.
Excessive Heat Input: The Pitfalls
An overdose of heat input can lead to cracks, distortion, and even melting of the base metal. It’s like pouring too much water into a teapot – it boils over and creates a mess. Excessive heat input weakens the weld by reducing the strength of the surrounding metal. It also increases the risk of distortion, as the heat causes the weld zone to expand and contract, leading to warped or misaligned pieces.
Insufficient Heat Input: The Other Extreme
On the flip side, insufficient heat input can result in incomplete fusion, poor penetration, and a brittle weld. It’s like trying to weld with a candle flame – the heat isn’t sufficient to melt the metal properly. This can lead to weak and unreliable welds that are more susceptible to cracking and failure.
Controlling Heat Input: The Key to Success
The secret to achieving optimal weld quality lies in controlling heat input. By manipulating three key variables – arc length, current, and speed – you can fine-tune the amount of heat delivered to the weld zone.
-
Arc Length: A shorter arc produces higher heat input, while a longer arc results in lower heat input. By adjusting the arc length, you can control the temperature of the weld zone and prevent overheating or underheating.
-
Current: Higher current increases heat input, while lower current decreases it. It’s analogous to the intensity of a flame – a stronger flame delivers more heat. By adjusting the current, you can control the amount of energy flowing into the weld zone.
-
Speed: The speed at which you weld also affects heat input. A slower travel speed allows more time for heat to transfer into the metal, resulting in higher heat input. Conversely, a faster travel speed reduces heat input. By adjusting the speed, you can control the heat distribution and prevent localized overheating.
Remember, heat input is the magic ingredient in welding. By understanding its importance and mastering the art of controlling it, you’ll unlock the secrets to consistently producing high-quality, reliable welds that will stand the test of time.
Assessing Weld Quality: A Crucial Aspect of Welding Excellence
In the realm of welding, achieving exceptional weld quality is paramount. This intricate process involves meticulous attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the welding arc’s fundamental parameters. Among these parameters, the arc voltage, current, length, penetration, travel speed, and heat input play critical roles. By optimizing these factors, welders can ensure the structural integrity, aesthetic appeal, and performance of their welds.
One of the most crucial aspects of weld quality is its strength and ductility. These attributes determine the ability of a weld to resist deforming or fracturing under various stresses. Destructive testing methods, such as tensile testing, provide valuable insights into the weld’s tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation.
Appearance is another key indicator of weld quality. A smooth, uniform weld with minimal spatters, porosity, and undercuts is aesthetically pleasing and indicates a well-executed welding process. Visual inspection techniques can reveal any surface imperfections or irregularities that may compromise the weld’s integrity.
Finally, performance evaluates the weld’s ability to withstand environmental factors, such as corrosion, fatigue, and extreme temperatures. Welders must consider the specific requirements of the application when selecting materials and optimizing welding parameters to ensure the weld’s long-term performance.
The welding arc parameters exert a profound influence on weld quality. Arc voltage, for instance, affects the arc’s stability, penetration, and overall weld characteristics. By adjusting the voltage, welders can achieve optimal heat distribution and minimize the risk of defects.
Arc current plays a pivotal role in controlling weld penetration, deposition rate, and arc stability. Higher currents typically result in deeper penetration, while lower currents favor wider welds. Striking the right balance between current and other parameters is essential for achieving the desired weld characteristics.
Arc length influences arc stability, heat distribution, and penetration. Maintaining a consistent arc length is crucial for achieving a uniform weld with optimal properties. Welders must adjust the arc length based on the thickness of the materials being welded and the specific requirements of the application.
By understanding the significance of welding arc parameters and their impact on weld quality, welders can develop the skills and expertise necessary to produce welds of unparalleled excellence. This mastery not only ensures the structural integrity of welded structures but also enhances their aesthetic appeal and performance, ultimately contributing to the success of the entire project.